| |
  |
 |
 |
 |
| |
|
|
| |
Finding functionally analogous enzymes based on the local structures of active sites is an important problem. Conventional methods use templates of local structures to search for analogous sites, but their performance depends on the selection of atoms for inclusion in the templates. The automatic selection of atoms so that site matches can be discriminated from mismatches. The algorithm provides not only good predictions, but also some insights into which atoms are important for the prediction. Our experimental results suggest that the metric learning automatically provides more effective templates than those whose atoms are selected manually. |
|
| |
 |
|
| |
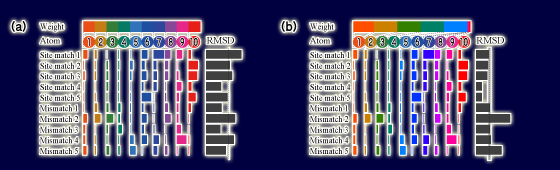
Example of metric learning. Computing RMSD is a typical means to search for site matches from numerous hits aligned with a query template. It involves taking the unweighted average of distances of each atom. This toy example shows a case in which each of the five site matches and five mismatches is aligned with a query template having 10 atoms. In this case, no threshold separates site matches from mismatches perfectly as long as the average of distances is unweighted, as shown in (a). Three mismatches and two site matches can be predicted incorrectly if the threshold depicted in (a) is used. Our metric learning algorithm finds a weight for each atom to generate a distance that separates site matches from mismatches. For this example, weighted RMSD supports a complete separation of site matches from mismatches, as shown in (b).
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
References |
|
| |
[17] Tsuyoshi Kato and Nozomi Nagano: Metric Learning for Enzyme Active-Site Search, Bioinformatics, Vol.26, No.21, pp.2698-2704 (2010), [pdf]. |
|
| |
[18] Tsuyoshi Kato, Kazuhiro Suwa and Nozomi Nagano: Parametric Templates: A New Enzyme Active-Site Prediction Algorithm. In conjunction with the 10th IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM 2010) Biological Data Mining and its Applications in Healthcare. |
|
| |
[19] Tsuyoshi Kato and Nozomi Nagano: Discriminative Structural Approaches for Enzyme Active-Site Prediction. BMC Bioinformatics, Vol 12(Supple 1), S49, presented at The Ninth Asia Pacific Bioinformatics Conference (APBC2011). |
|
| |
[xx] Nozomi Nagano, Naoko Nakayama, Kazuyoshi Ikeda, Masaru Fukuie, Kiyonobu Yokota, Takuo Doi, Tsuyoshi Kato, Kentaro Tomii, EzCatDB: the enzyme reaction database, 2015 update, Nucleic Acids Research,43(Database issue):D453-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku946, Jan 28, 2015. |
|
|
|
|
|
